Join Our Telegram Channel
Join Our Whatsapp Group
Thursday, 16th May 2024
Agricultural Science 2 (Essay) 2:00pm – 4:10pm
Agricultural Science 1 (Objective) 4:10pm – 5:00pm
AGRIC OBJ:
1-10: CBDBBBBCCA
11-20: CBCBCDDCDC
21-30: DCCDBABDDB
31-40: CBDDBAACAC
41-50: DBCDCBBBAB
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
(1ai)
Cooperative Farming:
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Enhanced market access
(ii) Increased Access to Credit
(iii) Provision of agricultural education and training
(iv) Risk management support
(1aii)
Farm Settlement Scheme:
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Improved access to land
(ii) Infrastructure Development
(iii) Development of essential infrastructure
(iv) Employment Generation
(v) Fostered community development through the provision of social amenities
(1aiii)
Agricultural Research Institute:
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Development of Improved Crop Varieties
(ii) They introduce and promote innovative farming techniques and technologies
(iii) Identification and controlling agricultural pests and diseases
(iv) It helped in policy Support and Advocacy
(1bi) Dibber:
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) Seed Drill
(ii) Planter
(1bii) Hoe:
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) Rotary Hoe
(ii) Cultivator
(1biii) Sickle:
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) Mower
(ii) Reaper.
(1biv) Wheelbarrow:
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) Trailer
(ii) Front Loader
(1bv) Watering Can:
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) Sprayer
(ii) Irrigation System
(1ci)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) The mouldboard plough effectively turns over the soil, burying crop residues and weeds, which helps to prepare a clean seedbed.
(ii) By turning the soil, the plough improves aeration, which enhances root growth and microbial activity.
(iii) The ploughing process helps to break up compacted soil, improving water infiltration and reducing surface runoff.
(iv) Burying crop residues and weeds helps to control pests and diseases, as well as reduce weed competition for the upcoming crop.
(1cii)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Repeated use of the mouldboard plough can lead to increased soil erosion, particularly on sloped land, due to the disturbance of soil structure.
(ii) Ploughing can cause a significant loss of soil moisture, which may negatively impact seed germination and crop growth in dry conditions.
(iii) Operating a mouldboard plough requires substantial power, which translates into higher fuel consumption and operational costs.
(iv) Over time, the use of heavy machinery for ploughing can lead to soil compaction, particularly in the subsoil, which can restrict root growth and reduce crop yields.
(2a)
[DRAW THE DIAGRAM OF SOIL PH]
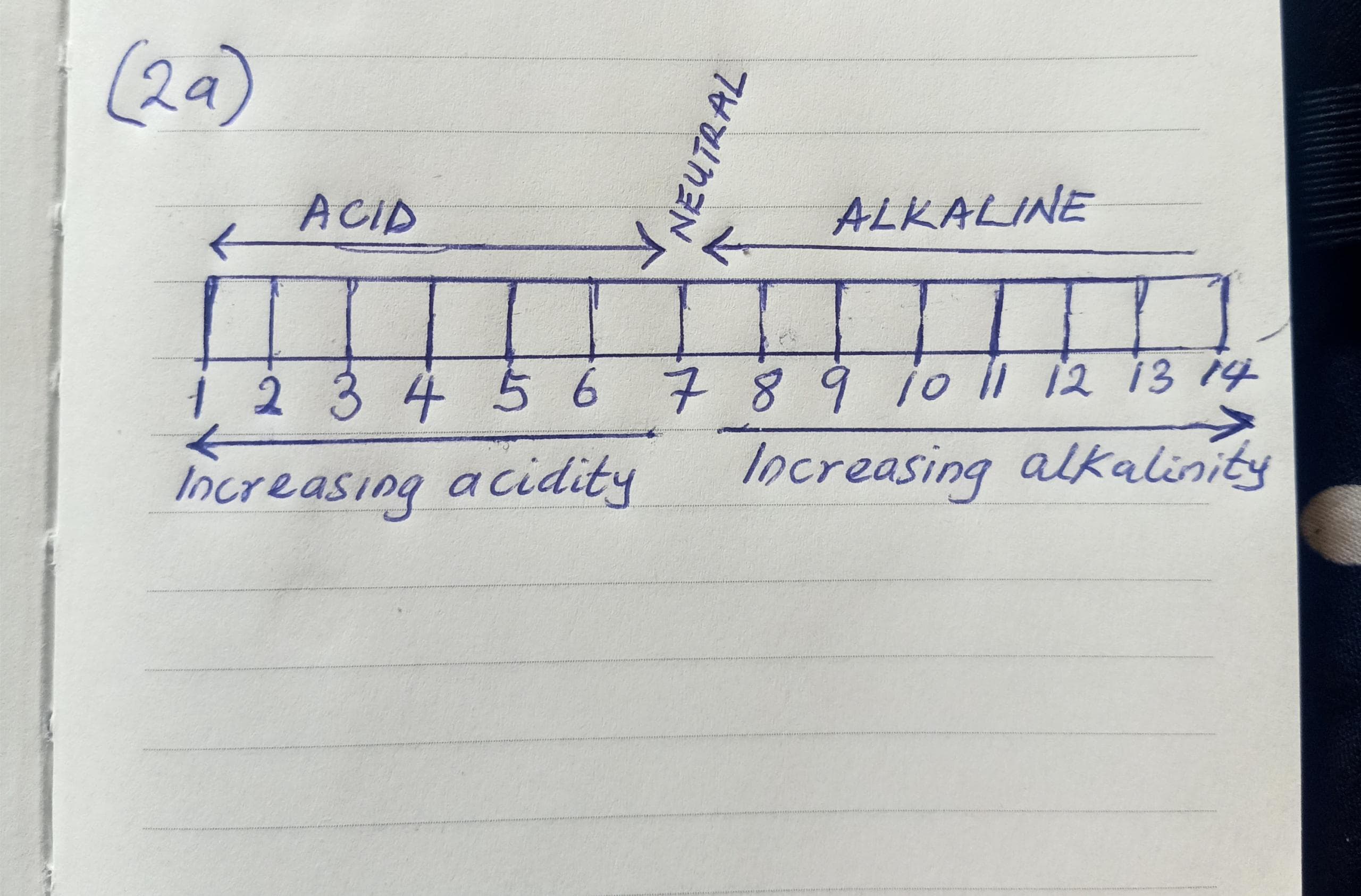
Soil pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of soil, expressed on a scale from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral, values below 7 indicate acidic soil, and values above 7 indicate alkaline soil.
(2bi)
Cover crops are plants grown primarily to protect and enrich soil during periods when main crops are not planted. They help prevent erosion, improve soil health, and manage weeds and pests.
(2bii)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) It prevents soil erosion.
(ii) It improves soil fertility.
(iii) It enhances soil structure.
(iv) It suppresses weeds.
(v) It manages pests and diseases.
(vi) It increases biodiversity.
(vii) It enhances water retention and management.
(2c)
(i) Wild marigold: Tagetes minuta
(ii) Spear grass: Heteropogon contortus
(iii) Stubborn grass: Sida acuta
(iv) Pigweed: Amaranthus retroflexus
(v) Carpet grass: Axonopus fissifolius
(3ai)
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) It fixes atmospheric nitrogen into soil
(ii) It produces nodules on legume roots
(3aii)
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) It oxidizes ammonia to nitrite
(ii) It initiates nitrification process
(3aiii)
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) It decomposes organic matter
(ii) It produces antibiotics and growth hormones
(3aiv)
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) It oxidizes nitrite to nitrate
(ii) It completes nitrification process
(3bi)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Distorted or curled leaves
(ii) Reduced plant growth and yield
(iii) Honeydew secretion attracting ants and other insects
(iv) Transmission of plant viruses
(v) Weakened plant defense against other pests and diseases
(3bii)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Planting resistant varieties
(ii) Removing weeds and debris
(iii) Pruning infested areas
(iv) Using crop rotation and intercropping
(v) Spraying water to dislodge aphids
(vi) Applying insecticidal soap or neem oil
(3ci)
Forestry is the management and conservation of forests for sustainable use, protection, and regeneration.
(3cii)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Timber (wood)
(ii) Fuelwood (firewood)
(iii) Pulp and paper products
(iv) Rubber
(v) Resins and gums
(vi) Medicinal plants and herbs
(vii) Wildlife and game meat
(4ai)
Area of farmland in hectares:
Area = Length × Width
Area = (300 m × 150 m) / 10,000 m²/hectare
Area = 4.5 hectares
(4aii)
The quantity of sorghum seeds required for planting:
Seed rate per hectare = 60 kg
Quantity of seeds = Seed rate per hectare × Area
Quantity of seeds = 60 kg/hectare × 4.5 hectares
Quantity of seeds = 270 kg
(4aiii)
The quantity of fertilizer required:
Fertilizer rate per hectare = 20 kg
Quantity of fertilizer = Fertilizer rate per hectare × Area
Quantity of fertilizer = 20 kg/hectare × 4.5 hectares
Quantity of fertilizer = 90 kg
(4bi)
(PICK ANY TWO)
Budding involves inserting a bud from one plant onto another, while grafting involves attaching a stem from one plant onto another plant.
(ii)Budding is typically done during the growing season, while grafting can be done during the growing season or dormant season.
(iii)Budding is requires less skill compared to grafting, which can be more complex and requires precise alignment for successful union.
(iv)In budding, only a single bud is used, whereas in grafting, a portion of stem with multiple buds is attached
(4bii)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Grapefruit
(ii) Apples
(iii) Oranges
(iv) Lemon
(v) Peaches
(vi) Plums
(4ci)
Production ration:
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i)Lactating dairy cows
(ii)Laying hens
(iii)Breeding sows (female pigs)
(iv)Turkeys in the finishing stage for meat production
(4cii)
Maintenance ration:
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i)Mature beef cattle
(ii)Adult sheep
(iii)Non-lactating dairy cows
(iv)Breeding bulls
(5ai)
Removal of excessive vegetation:
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i)Enhances oxygen levels by reducing competition for dissolved oxygen.
(ii)Prevents the accumulation of organic matter, which can lead to water quality issues.
(iii)Reduces the risk of predators finding hiding spots.
(iv)Improves water circulation and sunlight penetration, promoting overall pond health.
(5aii)
Removal of silt:
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i)Prevents the accumulation of bottom sediments
(ii)Maintains adequate water depth, crucial for fish growth and reproduction.
(iii)Improves water clarity, allowing sunlight to penetrate and promoting aquatic plant growth.
(iv)Prevents the depletion of oxygen due to decomposition of organic matter in the silt.
(5aiii)
Supplementary feeding:
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i)Stimulates faster fish growth and development.
(ii)Compensates for deficiencies in natural food sources.
(iii)Allows for controlled nutrient input, promoting optimal fish health.
(iv)Maximizes fish production and profitability of the fish farming operation
(5aiv)
Fertilizer application:
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i)Stimulates the growth of phytoplankton, a vital food source for fish.
(ii)Enhances nutrient cycling and productivity in the pond ecosystem.
(iii)Increases overall fish yield by supporting the entire food chain.
(iv)Helps maintain water quality by promoting biological processes that consume excess nutrients.
(5b)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i)Disease outbreaks to prevent further spread.
(ii)Overpopulation leading to resource depletion and stress.
(iii)Poor growth performance or genetic defects.
(iv)Aggressive behaviour endangering other animals or humans.
(v)Non-productivity, such as infertility or inability to produce desired products.
(vi)Economic factors like market demand or changes in production goals.
(5c)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i)Nitrogen toxicity leading to stunted growth or leaf burn.
(ii)Increased susceptibility to diseases and pests.
(iii)Imbalance in nutrient uptake, affecting overall plant health.
(iv)Reduced yield quality, such as lower protein content in grains.
(v)Environmental pollution through leaching or runoff into water bodies.
(vi)Disruption of soil microbial communities, affecting nutrient cycling and soil structure.
(6a)
Agricultural insurance provides financial protection to farmers against losses incurred due to natural disasters, crop failure, or other unforeseen events
(6bi)
Insurance policy: Insurance policy is a legal contract between the insurer and the insured that outlines the terms and conditions of coverage, including the risks covered, the duration of coverage, and the amount of compensation in case of loss or damage.
(6ii)
Insurance premium: Insurance premium is the amount of money paid by the insured to the insurance company in exchange for coverage under the insurance policy.
(6ci)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i)Facilitates direct interaction between farmers and experts.
(ii)Enables personalized assistance tailored to specific farming needs.
(iii)Promotes knowledge sharing and exchange of best practices among farmers.
(iv)Helps disseminate new technologies and innovations to improve agricultural practices.
(v)Builds trust and strengthens relationships between farmers and agricultural authorities.
(vi)Increases farmers’ capacity to adapt to challenges and improve productivity sustainably.
(6cii)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i)Farmer field days or agricultural fairs.
(ii)Radio broadcasts or agricultural programs.
(iii)Mobile phone text messages or voice calls.
(iv)Pamphlets or printed materials distributed door-to-door.
(v)Demonstration plots or on-farm training sessions.
(6d)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i)Threshing: Separating the rice grains from the stalks or straw.
(ii)Winnowing: Removing the chaff and debris from the rice grains through air currents.
(iii)Drying: Reducing the moisture content of the rice grains
(iv)Cleaning: Removing impurities, such as stones, dirt
(v)Milling: Removing the outer layers of the rice grain.
(vi)Polishing: Buffing the rice grains to enhance appearance and marketability.
Answers Loading...





